O Jogo da Construção Enxuta Technion LEAPCON™ simula a construção de um edifício de oito andares com quatro apartamentos por andar. Foi inicialmente desenvolvido para testar o impacto do modelo proposto de gestão Enxuta, que é uma resposta ao desperdício relacionado aos métodos convencionais de planejamento e gerenciamento da construção de edifícios residenciais muito altos. Provou-se ser uma excelente ferramenta de introdução a alguns conceitos básicos de construção enxuta para gerentes, engenheiros de obra, supervisores, gerentes-sêniores e estudantes: construçãode uma unidade por vez versus fluxo contínuo, planejamento e controle puxado versus empurrado e equipes multi-tarefas versus equipes especializadas.
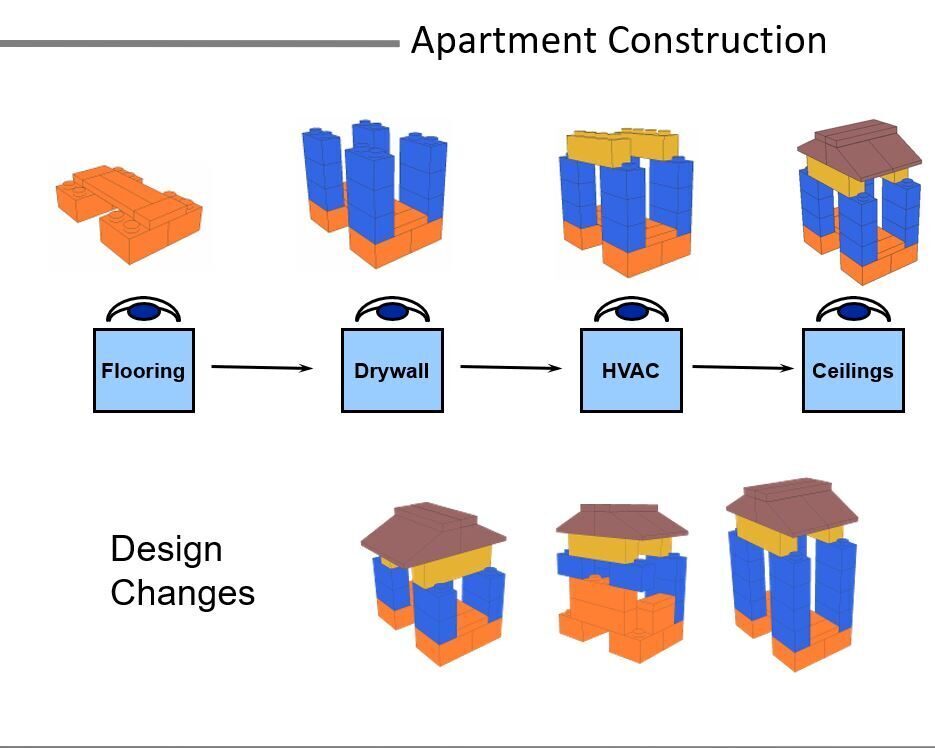
Os participantes assumem os papéis de: gerente de projetos, gerente comercial, gerente da qualidade, operador de grua, além de quatro diferentes empreiteiras. O trabalho deles é finalizar a montagem dos interiores dos 32 apartamentos no menor tempo possível. A execução dos trabalhos é simulada através da montagem de pequenos edifícios usando blocos de LEGO (ver Fig. 1); elessão montados em quatro passos distintos, cada um assumido por uma das quatro empreiteiras. Outros dois jogadores representam os clientes dos apartamentos – o primeiro escolhe mudanças no design a partir de sete variações prédefinidas, e o segundo confere se os apartamentos estão completos e paga $1500,00 para cada apartamento construído sem defeitos.
Figura 1. O apartamento padrão. Os passos da montagem representam o assentamento de pisos (laranja), paredes divisórias (azul), cabeamento elétrico (amarelo) e forros acústicos (marrom).
Na primeira rodada, que dura 11 minutos, o gerente de projetos recebe um planejamento de obra que demanda que as empreiteiras ataquem o edifício andar por andar, um após o outro, na sequêncialógica relacionada às dependências técnicas de cada especialidade. O tamanho do lote de serviço é 4 unidades, o que quer dizer que somente um empreiteira pode entrar em um andar por vez. Emintervalos determinados, durante a obra, os clientes pedem alterações de projeto, escolhendo aleatoriamente um apartamento e uma opção de design, e entregam o pedido à ‘construtora’. As alterações de projeto que são recebidas antes do início do trabalho em um apartamento são facilmente executadas, embora causem uma turbulência no fluxo de trabalho, pois necessitam de um tempo maior para serem aplicadas.
Apartamentos que recebem pedidos de alteração de projetos depois que o trabalho começou, mas antes de serem entregues ao cliente, precisam ser executados. O gerente de projetos precisa decidirse tira a empreiteira do andar em que ela está trabalhando e pede que ela vá fazer a alteração imediatamente, ou que faça a alteração posteriormente. O fator chave para as tomadas de decisão é que a construtora só recebe por apartamento entregue completo, enquanto é necessário investir capital ($1000,00) para qualquer apartamento iniciado, mesmo que incompleto. O jogo é interrompido depoisde 11 minutos, e a performance da equipe é avaliada com relação aos apartamentos entregues, quantidade de trabalho incompleto (WIP), fluxo de caixa, apartamentos com baixa qualidade de entregae o tempo para a conclusão do primeiro apartamento com projeto fora do padrão. Os resultados medidos a partir dos trabalhos realizados por sete grupos estão exibidos nas tabelas 1 & 2 abaixo.
Na segunda rodada, são feitas as seguintes alterações nas regras:
1. O planejamento puxado substitui o empurrado – a sequência de trabalho é alterada, em que as alterações de projetos pedidas pelos clientes é que determinam a ordem de execução (o trabalho sócomeça após a definição das alterações de projeto).
2. As quatro empreiteiras especialistas são substituídas por quatro empreiteiras multi-especializadas, que podem executar todas as atividades.
3. O tamanho do lote de serviço é reduzido de quatro unidades para uma.
Todas as outras condições de projeto permanecem como antes. Os resultados típicos para esta rodada, obtidos a partir dos mesmos sete grupos, estão listados na Tabela 4. Como pode serobservado, a produtividade é quase dobrada, há uma redução drástica na quantidade de trabalhos incompletos (como em todos os sistemas puxados, que são bem controlados), assim como os ciclosde obra, e como resultado o fluxo de caixa se torna positivo.
Tabela 1. Média dos resultados da rodada 1, 11 repetições: processo Convencional
| Apartamentos completados | Apartamentos com defeito | Tempo para completar o primeiro apartamento (min.) | Trabal hosinc ompletos(WIP) | Velocidade da entrega(unidades/min) | Fluxo de caixa | Ciclo da obra(min.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.0 | 0.57 | 6:35 | 13.4 | 1.12 | ($9,429) | 6:00 |
Tabela 2. Média dos resultados da rodada 2, 11 repetições: processo Enxuto
| Apartamentos completados | Apartamentos com defeito | Tempo para completar o primeiro apartamento (min.) | Trabal hosin completos(WIP) | Velocidade da entrega(unidades/min) | Fluxo de caixa | Ciclo da obra(min.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15.6 | 0.00 | 2:49 | 2.3 | 2.30 | $5,500 | 1:21 |

Some of the leading lights of lean construction playing the Technion LEAPCON™ game (from left to right; Tariq Abdelhamid, Carlos Formoso, Fritz Gehbauer, Ken Walsh, Lauri Koskela, Glenn Ballard)
How to obtain the game
The Technion LEAPCON™ game is available free of charge for academic use in a university, or for a small fee for commercial use. The package includes complete step by step instructions for each role, playing cards, ordering list for Lego® bricks, and directions for facilitators. To obtain the game, please e-mail Dr. Rafael Sacks.
The game is available in English, Russian and Spanish versions.
Bibliography
- Sacks, R., and Goldin, M., (2007). ‘Lean Management Model for Construction of High-rise Apartment Buildings’, ASCE Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, Vol. 133 No. 5 pp. 374-384.
- Sacks, R., Esquenazi, A., and Goldin, M., (2007). “Simulation of Lean Construction Management of High-rise Apartment Buildings”, ASCE Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, Vol. 133 No. 7 pp. 529-539.
- Sacks, R., Goldin, M., and Derin, Z. (2005). ‘Pull-driven construction of high-rise apartment buildings’ Proceedings of the 13th Conference of the International Group for Lean Construction, R. Kenley (Ed.), Sydney, Australia, pp. 217-226.
- Esquenazi, A., and Sacks, R., (2006). ‘Evaluation of Lean Improvements in Residential Construction using Computer Simulation’, Understanding and Managing the Construction Process: Theory and Practice, Proceedings of the 14th Conference of the International Group for Lean Construction, R. Sacks and S. Bertelsen, (Eds.), Santiago, Chile, pp.137-149.
- Sacks, R., and Derin, Z., (2006). ”WORKMANAGER’ – an Online Interface for Lean Flow Control in Apartment Building Construction’, ICCCBE-XI – 11th Int’l Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering, H. Rivard and E. Miresco, (Eds.), Montreal, Canada, pp. 1176-1185.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
- I have a query on the game related to the CONVENTIONAL ROUNDFor example, if an apartment is being built to a the Standard Design (A) and the flooring, partition and the HVAC duct work has been completed. After this completion design change calls for Design (F) ie. Partition has to be changed/ Ceiling is rotated 90 degree. What is the correct procedure?
- a) Will the partition contractor come and he will remove the duct and then modify the partition. After that reassemble the duct, OR
- b) First ask the duct sub contractor to dismantle the duct, then the partition contractor to modify the partition and then the duct contractor again to refix the dismantled duct.
What is your advice in playing in such a situation.
Rajiv Misra, XLRI, India
Strictly speaking, solution b) is the correct one. However, we are all human, and I have found that when the pressure is on, and the players feel that they are trying to compete with the clock, then sometimes they have trouble sticking to this rule, and they act as you described in a).
I have found that it makes only a small difference; but I have always made a point to explain to them in the summary discussion after the conventional round that exactly that kind of situation arises in real buildings. What happens then is that either the partitioning subcontractor says ‘Hey, it’s not my job to undo the ductwork!!’ and the project is delayed, or the project manager insists that they do undo the ductwork to avoid delay, and then damage night be done. Either way, it reinforces the participants understanding of how specialization of tasks in construction has such a detrimental effect on flow when changes are common.
- Quick question — what would you say is the minimum time to play the game ? I have 1h15m in my class.Bill O’Brien, Texas A&M, USAAbout 1h45m has been the minimum time when running the game in a single session, although the smaller the group the quicker it can be set up and run – it depends a lot on how much explanation and background you need to provide them on lean production/construction before you begin the game itself.For a 1h15min session, I recommend splitting it into two. During the first session, you could provide background, explain the setup, and run the first round comfortably. Then, in a following session, you would need about 45m to do the second round and to debrief them. You could even pose a ‘homework’ challenge after the first session that the students should try to come up with an alternative management scheme and submit it before they actually are told the rules of the second round and do it. I have considered at times whether to allow an intermediate round in which the students design a system and then implement it, before showing them the benefits of pull flow, single piece flow and multi-skilling; that is something you could implement at the start of a second session.
- I have a query on the game related to the CONVENTIONAL ROUNDFor example, if an apartment is being built to a the Standard Design (A) and the flooring, partition and the HVAC duct work has been completed. After this completion design change calls for Design (F) ie. Partition has to be changed/ Ceiling is rotated 90 degree. What is the correct procedure?
- I have seen in one of the videos (The Tidhar way http://youtu.be/2gGgCL4ZQUo ) that “The team decided to let go of the project manager and hire a second quality assurance”. In addition to this, I see that every player has a stacked amount of pieces in front of him. Did they prepare the “stock” before?Filippo Bossi, Università degli Studi di Firenze – Department of Architecture The Tidhar group had run the game a number of times, and they were trying to perfect it. They were free, in this third round, to reassign tasks within the contracting company, with one condition: they were not allowed to increase the number of production workers. Only four are allowed, the same in all rounds. They identified that the project manager was under-employed in the second round, so they assigned him to help with the quality control. Most groups do not think of this the first time they play the second round, but if you have time and you decide to play a third round, then you can challenge them to think of further improvements such as this.The tower crane and the material transport are not the main focus of the game, and so I usually do not object, if there ius a third round, that they pre-prepare piles of material close to the work place.
LEAPCON users
| Country | Educational | Industrial or Governmental |
|---|---|---|
 |
| |
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
| |
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
 |

Resources